Design Thinking is an approach to problem solving that focuses on empathy for the user and understanding their needs, team collaboration, generating ideas and seeing how things work in practice.
This requires understanding users, questioning assumptions, redefining problems, and creating innovative solutions. It focuses on solving the problem, not just the problem itself.
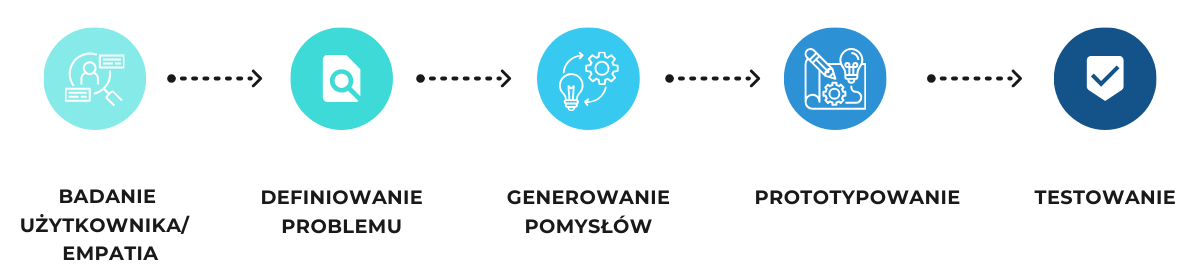
This process typically consists of five phases: empathy, problem definition, ideation, prototyping, and testing.
The Design Thinking method emphasizes empathy, collaboration, and creativity, which contributes to the development of students' soft skills. By introducing Design Thinking into academic teaching, an environment can be created that encourages innovative thinking, collaboration, and effective problem-solving.


The advantages of using Design Thinking include:
- Supporting creativity and creative activities of students, for example, through the use of brainstorming methods.
- Introducing students to project work methodology.
- Improving collaboration skills and strengthening relationships through group work.
- Building empathy among students and understanding the needs and experiences of the user, which is particularly important in engineering work, such as in universal design.
- Solutions developed through Design Thinking are more focused on the real needs and expectations of users.
- The possibility of applying the method in various contexts and during classes from different subjects (e.g., mechanical engineering, architecture, management). Its universality means it can be adapted to different fields and problems.
The advantages of the Design Thinking method make it attractive to designers and entrepreneurs, as well as to academic teachers, by supporting the creative problem-solving process and developing skills essential in the job market.
- Design Thinking requires time for research, ideation, prototyping, and testing. In an academic environment, where there is often an emphasis on delivering curriculum content, it can be challenging to find enough time to fully implement this approach.
- Implementing Design Thinking may require access to diverse resources such as space for team collaboration, materials for prototyping, and tools for research and data analysis. A lack of these resources can be a barrier to effectively applying the method.
- An excessive emphasis on creativity and experimentation can lead to a lack of structure in the process. Consequently, the project may become stalled in the ideation phase, without concrete actions towards a solution..
Literature/More Information:
Harvard Business School, What Is Design Thinking & Why Is It Important?, https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/what-is-design-thinking
Interaction Design Foundation, What Is Design Thinking?, https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/design-thinking
Interaction Design Foundation, What Is Design Thinking and why is it so popular?, https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/what-is-design-thinking-and-why-is-it-so-popular
IDEOU, https://www.ideou.com/blogs/inspiration/what-is-design-thinking
Fundacja szkoła z klasą, Design thinking w edukacji, https://www.szkolazklasa.org.pl/materialy/desigh-thinking-edukacji/